Web Server
We can add an application layer or a protocol layer on top of Reactor to build a web server. The Reactor we built in A Million Concurrency handles I/O events at the network layer. While it currently only echos what the client sends, we will extend it by adding support for HTTP and WebSocket protocols.
HTTP Server
Handle HTTP Requests
We split tcp_server.c into two components: reactor.c, which handles I/O events
at the network layer using Reactor, and webserver.c, which manages application-layer
protocols.
#ifndef SERVER_H
#define SERVER_H
#define BUFFER_LENGTH 1024
typedef int (*RCALLBACK)(int fd);
// fd and its callbacks, along with buffers to support cbs
struct connection {
int fd;
char rbuffer[BUFFER_LENGTH];
int rlength;
char wbuffer[BUFFER_LENGTH];
int wlength;
RCALLBACK send_callback;
// handle EPOLLIN
// for listen_fd it's used for accepting connection
// for client_fd it's used for receiving data
RCALLBACK recv_callback;
};
int http_request(struct connection *);
int http_response(struct connection *);
#endif
#include <signal.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/epoll.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include "server.h"
// the client will try to create a million conection
// the connection size needs to be bigger than a million
// because we are also using fd as index and new fd doesn't
// start from 0
#define CONNECTION_SIZE 1012000
// for port cycling
#define MAX_PORTS 30
#define TIME_SUB_MS(tv1, tv2) ((tv1.tv_sec - tv2.tv_sec) * 1000 + (tv1.tv_usec - tv2.tv_usec) / 1000)
struct timeval ts;
int listen_fds[MAX_PORTS] = {0};
void handle_signal(int sig) {
int i;
printf("\nserver closing...\n");
for (i = 0; i < MAX_PORTS; i++) {
int fd = listen_fds[i];
if (fd > 0) {
printf("[%d] closing fd %d\n", i, fd);
close(fd);
};
}
printf("bye\n");
exit(0);
}
int init_server(unsigned int port) {
int listen_fd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
if (listen_fd == -1) {
perror("socket");
return -1;
}
// define server address: ip + port
struct sockaddr_in server_addr;
server_addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
server_addr.sin_port = htons(port);
server_addr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY);
// bind and listen for connection
int status = bind(listen_fd, (struct sockaddr *) &server_addr, sizeof(server_addr));
if (status == -1) {
perror("bind socket");
return -1;
}
listen(listen_fd, 10); // allows 10 queued connections
return listen_fd;
}
int epfd;
int accept_cb(int);
int recv_cb(int);
int send_cb(int);
// where we define fd and its callbacks for handling events
// use fd as index
struct connection connection_list[CONNECTION_SIZE] = {0};
// flag determines whether ADD (if non-zero) or MODIFY
int set_event(int fd, int events, int flag) {
int ctl;
if (flag) ctl = EPOLL_CTL_ADD;
else ctl = EPOLL_CTL_MOD;
struct epoll_event ev;
ev.events = events;
ev.data.fd = fd;
return epoll_ctl(epfd, ctl, fd, &ev);
}
int register_event(int fd, int events) {
if (fd < 0) return -1; // otherwise may get "Segmentation fault (core dumped)"
connection_list[fd].fd = fd;
connection_list[fd].recv_callback = recv_cb;
connection_list[fd].send_callback = send_cb;
// reset buffers since fd can be reused
memset(connection_list[fd].rbuffer, 0, BUFFER_LENGTH);
connection_list[fd].rlength = 0;
memset(connection_list[fd].wbuffer, 0, BUFFER_LENGTH);
connection_list[fd].wlength = 0;
// listen for event (readability)
set_event(fd, events, 1);
return 0;
}
int connections = 0;
int accept_cb(int fd) { // listen_fd
struct sockaddr_in client_addr;
socklen_t len = sizeof(client_addr);
int client_fd = accept(fd, (struct sockaddr *)&client_addr, &len);
if (client_fd == -1) {
perror("accept");
return -1;
}
register_event(client_fd, EPOLLIN);
connections++;
// shows the number of connections
// and the time to create them
if (connections % 1000 == 0 || connections > (CONNECTION_SIZE - 1000)) {
struct timeval now;
gettimeofday(&now, NULL);
int ts_elapsed = TIME_SUB_MS(now, ts);
memcpy(&ts, &now, sizeof(struct timeval));
printf("number of connections: %d, time elapsed: %dms\n", connections, ts_elapsed);
}
return 0; // success
}
int recv_cb(int fd) {
int count = recv(fd, connection_list[fd].rbuffer, BUFFER_LENGTH, 0);
if (count == 0) { // EOF, close connection
printf("disconnect fd %d\n", fd);
close(fd);
epoll_ctl(epfd, EPOLL_CTL_DEL, fd, NULL);
return 0;
}
connection_list[fd].rlength = count;
// replaced with http_request handler below
// echo to wbuffer (response)
// connection_list[fd].wlength = count;
// memcpy(connection_list[fd].wbuffer, connection_list[fd].rbuffer, connection_list[fd].wlength);
http_request(&connection_list[fd]);
set_event(fd, EPOLLOUT, 0); // modify
// clear the read buffer for the next read otherwise it may contains data from the last ready
memset(connection_list[fd].rbuffer, 0, BUFFER_LENGTH);
return count;
}
int send_cb(int fd) {
// set wbuffer with http handler
http_response(&connection_list[fd]);
int count = send(fd, connection_list[fd].wbuffer, connection_list[fd].wlength, 0);
set_event(fd, EPOLLIN, 0); // modify, fd is already in epoll instance
return count;
}
int main() {
signal(SIGPIPE, SIG_IGN); // trap broken pipes
signal(SIGINT, handle_signal); // handle Ctrl+C (SIGINT)
gettimeofday(&ts, NULL);
unsigned short port = 8001;
epfd = epoll_create(1);
int i;
for (i = 0; i < MAX_PORTS; i++) {
int listen_fd = init_server(port + i);
if (listen_fd == -1) return -1;
listen_fds[i] = listen_fd; // register for cleanup
connection_list[listen_fd].fd = listen_fd;
connection_list[listen_fd].recv_callback = accept_cb;
set_event(listen_fd, EPOLLIN, 1);
}
while(1) { // main loop
struct epoll_event events[1024] = {0};
int nready = epoll_wait(epfd, events, 1024, -1);
int i;
for (i = 0; i < nready; i++) {
int fd = events[i].data.fd;
// may handle read and write in the same iteration
if (events[i].events & EPOLLIN) {
connection_list[fd].recv_callback(fd); // either accept or recv depending on lt's listen_fd or client_fd
}
if (events[i].events & EPOLLOUT) {
connection_list[fd].send_callback(fd);
}
}
}
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/sendfile.h>
#include "server.h"
// define the root directory of the webserver
// it's used to locate resources
#define WEBSERVER_ROOTDIR "./"
int http_request(struct connection *c) {
printf("request: %s\n", c->rbuffer);
// reset wbuffer (http response)
memset(c->wbuffer, 0, BUFFER_LENGTH);
c->wlength = 0;
return 0;
}
int http_response(struct connection *c) {
// contruct http response and write it to wbuffer for sending
c->wlength = sprintf(c->wbuffer,
"HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\n"
"Content-Type: text/html\r\n"
"Accept-Ranges: bytes\r\n"
"Content-Length: 78\r\n" // the length of http body
"Date: Thu, 16 Jan 2025 17:52:35 GMT\r\n\r\n" // in RFC 7231 format, end of http header
"<html><head><title>hello</title></head><body><p>hello me</p></body></html>\r\n\r\n" // http body
);
return c->wlength;
}
When an HTTP request arrives from the browser, the rbuffer is populated
by the network layer (I/O event handled by Reactor). We then delegate
reading from rbuffer to the protocol layer, which processes it using http_request.
For now, we simply print out the request and prepare the wbuffer for the response.
Send multiple times
For a larger file like an image, it may make more sense to break it into multiple parts
and send it multiple times. WE can achieve this by adding a state status to the connection.
State machine: stateful connection handling
#ifndef SERVER_H
#define SERVER_H
#define BUFFER_LENGTH 1024
typedef int (*RCALLBACK)(int fd);
// fd and its callbacks, along with buffers to support cbs
struct connection {
int fd;
char rbuffer[BUFFER_LENGTH];
int rlength;
char wbuffer[BUFFER_LENGTH];
int wlength;
RCALLBACK send_callback;
// handle EPOLLIN
// for listen_fd it's used for accepting connection
// for client_fd it's used for receiving data
RCALLBACK recv_callback;
// the status of this connection
// 0: initial state
// 1: wbuffer ready for the first send
// 2: continue to send other parts
int status;
};
int http_request(struct connection *);
int http_response(struct connection *);
#endif
#include <signal.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/epoll.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include "server.h"
// the client will try to create a million conection
// the connection size needs to be bigger than a million
// because we are also using fd as index and new fd doesn't
// start from 0
#define CONNECTION_SIZE 1012000
// for port cycling
#define MAX_PORTS 30
#define TIME_SUB_MS(tv1, tv2) ((tv1.tv_sec - tv2.tv_sec) * 1000 + (tv1.tv_usec - tv2.tv_usec) / 1000)
struct timeval ts;
int listen_fds[MAX_PORTS] = {0};
void handle_signal(int sig) {
int i;
printf("\nserver closing...\n");
for (i = 0; i < MAX_PORTS; i++) {
int fd = listen_fds[i];
if (fd > 0) {
printf("[%d] closing fd %d\n", i, fd);
close(fd);
};
}
printf("bye\n");
exit(0);
}
int init_server(unsigned int port) {
int listen_fd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
if (listen_fd == -1) {
perror("socket");
return -1;
}
// define server address: ip + port
struct sockaddr_in server_addr;
server_addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
server_addr.sin_port = htons(port);
server_addr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY);
// bind and listen for connection
int status = bind(listen_fd, (struct sockaddr *) &server_addr, sizeof(server_addr));
if (status == -1) {
perror("bind socket");
return -1;
}
listen(listen_fd, 10); // allows 10 queued connections
return listen_fd;
}
int epfd;
int accept_cb(int);
int recv_cb(int);
int send_cb(int);
// where we define fd and its callbacks for handling events
// use fd as index
struct connection connection_list[CONNECTION_SIZE] = {0};
// flag determines whether ADD (if non-zero) or MODIFY
int set_event(int fd, int events, int flag) {
int ctl;
if (flag) ctl = EPOLL_CTL_ADD;
else ctl = EPOLL_CTL_MOD;
struct epoll_event ev;
ev.events = events;
ev.data.fd = fd;
return epoll_ctl(epfd, ctl, fd, &ev);
}
int register_event(int fd, int events) {
if (fd < 0) return -1; // otherwise may get "Segmentation fault (core dumped)"
connection_list[fd].fd = fd;
connection_list[fd].recv_callback = recv_cb;
connection_list[fd].send_callback = send_cb;
// reset buffers since fd can be reused
memset(connection_list[fd].rbuffer, 0, BUFFER_LENGTH);
connection_list[fd].rlength = 0;
memset(connection_list[fd].wbuffer, 0, BUFFER_LENGTH);
connection_list[fd].wlength = 0;
// listen for event (readability)
set_event(fd, events, 1);
return 0;
}
int connections = 0;
int accept_cb(int fd) { // listen_fd
struct sockaddr_in client_addr;
socklen_t len = sizeof(client_addr);
int client_fd = accept(fd, (struct sockaddr *)&client_addr, &len);
if (client_fd == -1) {
perror("accept");
return -1;
}
register_event(client_fd, EPOLLIN);
connections++;
// shows the number of connections
// and the time to create them
if (connections % 1000 == 0 || connections > (CONNECTION_SIZE - 1000)) {
struct timeval now;
gettimeofday(&now, NULL);
int ts_elapsed = TIME_SUB_MS(now, ts);
memcpy(&ts, &now, sizeof(struct timeval));
printf("number of connections: %d, time elapsed: %dms\n", connections, ts_elapsed);
}
return 0; // success
}
int recv_cb(int fd) {
int count = recv(fd, connection_list[fd].rbuffer, BUFFER_LENGTH, 0);
if (count == 0) { // EOF, close connection
printf("disconnect fd %d\n", fd);
close(fd);
epoll_ctl(epfd, EPOLL_CTL_DEL, fd, NULL);
return 0;
}
connection_list[fd].rlength = count;
// echo to wbuffer (response)
// connection_list[fd].wlength = count;
// memcpy(connection_list[fd].wbuffer, connection_list[fd].rbuffer, connection_list[fd].wlength);
http_request(&connection_list[fd]);
set_event(fd, EPOLLOUT, 0); // modify
// clear the read buffer for the next read otherwise it may contains data from the last ready
memset(connection_list[fd].rbuffer, 0, BUFFER_LENGTH);
return count;
}
int send_cb(int fd) {
// prepare wbuffer for first send
// status will change from 0 (init) to 1 (ready)
http_response(&connection_list[fd]);
int count = 0;
if (connection_list[fd].status == 1) {
// first send
count = send(fd, connection_list[fd].wbuffer, connection_list[fd].wlength, 0);
set_event(fd, EPOLLOUT, 0); // listen for continued sends of other parts
} else if (connection_list[fd].status == 2) {
// continue to send, handled by sendfile inside http_response
set_event(fd, EPOLLOUT, 0); // listen for the completion of the send (continued sends)
} else if (connection_list[fd].status == 0) {
// send finished, listen for another http connection
set_event(fd, EPOLLIN, 0);
}
return count;
}
int main() {
signal(SIGPIPE, SIG_IGN); // trap broken pipes
signal(SIGINT, handle_signal); // handle Ctrl+C (SIGINT)
gettimeofday(&ts, NULL);
unsigned short port = 8001;
epfd = epoll_create(1);
int i;
for (i = 0; i < MAX_PORTS; i++) {
int listen_fd = init_server(port + i);
if (listen_fd == -1) return -1;
listen_fds[i] = listen_fd; // register for cleanup
connection_list[listen_fd].fd = listen_fd;
connection_list[listen_fd].recv_callback = accept_cb;
set_event(listen_fd, EPOLLIN, 1);
}
while(1) { // main loop
struct epoll_event events[1024] = {0};
int nready = epoll_wait(epfd, events, 1024, -1);
int i;
for (i = 0; i < nready; i++) {
int fd = events[i].data.fd;
// may handle read and write in the same iteration
if (events[i].events & EPOLLIN) {
connection_list[fd].recv_callback(fd); // either accept or recv depending on lt's listen_fd or client_fd
}
if (events[i].events & EPOLLOUT) {
connection_list[fd].send_callback(fd);
}
}
}
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/sendfile.h>
#include "server.h"
#define WEBSERVER_ROOTDIR "./"
// get the time as per RFC 7231
// e.g. Tue, 30 Apr 2024 13:16:46 GMT
int get_rfc7231_date(char *buffer, size_t buffer_size) {
time_t now = time(NULL); // get the current time
struct tm *gmt = gmtime(&now); // convert to GMT/UTC
if (gmt != NULL) {
// format the time as per RFC 7231
strftime(buffer, buffer_size, "%a, %d %b %Y %H:%M:%S GMT", gmt);
return 0;
} else {
// handle error
printf("failed to get time\n");
return 1;
}
}
int http_request(struct connection *c) {
printf("request: %s\n", c->rbuffer);
// reset wbuffer
memset(c->wbuffer, 0, BUFFER_LENGTH);
c->wlength = 0;
c->status = 0;
return 0;
}
int http_response(struct connection *c) {
int file_fd = open(WEBSERVER_ROOTDIR "coffee.png", O_RDONLY);
struct stat stat_buf;
fstat(file_fd, &stat_buf);
char date_buffer[128];
get_rfc7231_date(date_buffer, sizeof(date_buffer));
if (c->status == 0) {
c->wlength = sprintf(c->wbuffer,
"HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\n"
"Content-Type: image/png\r\n"
"Accept-Ranges: bytes\r\n"
"Content-Length: %ld\r\n"
"Date: %s\r\n\r\n",
stat_buf.st_size, date_buffer);
c->status = 1;
} else if (c->status == 1) {
// mmap is efficient but unfortunately
// buniness logic is now coupled with IO if we sendfile
int res = sendfile(c->fd, file_fd, NULL, stat_buf.st_size);
if (res == -1) {
perror("sendfile");
}
c->status = 2;
} else if (c->status == 2) {
c->wlength = 0;
memset(c->wbuffer, 0, BUFFER_LENGTH);
c->status = 0;
}
close(file_fd);
return c->wlength;
}
QPS testing
I performed QPS testing on my WSL2 with wrk
using a simple index.html (replacing the image mentioned earilier).
The QPS is much lower than I expected, even after disabling all the
printfs.
$ wrk -c50 -t10 -d10s http://0.0.0.0:8001
Running 10s test @ http://0.0.0.0:8001
10 threads and 50 connections
Thread Stats Avg Stdev Max +/- Stdev
Latency 49.73ms 3.59ms 52.98ms 99.49%
Req/Sec 99.83 13.57 151.00 88.48%
9877 requests in 10.05s, 3.25MB read
Requests/sec: 982.52
Transfer/sec: 331.54KB
Maybe I should revive my old ThinkPad 
WebSocket Server
Here’s a fixed and polished version of your sentence:
An example WebSocket handshake message is provided below, and the protocol is defined in The WebSocket Protocol.
received: GET / HTTP/1.1
Host: localhost:8001
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64; rv:134.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/134.0
Accept: */*
Accept-Language: en-US,en;q=0.5
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate, br, zstd
Sec-WebSocket-Version: 13
Origin: null
Sec-WebSocket-Extensions: permessage-deflate
Sec-WebSocket-Key: 7MOhe0nRW4N3W1wJ8FrF+A==
Connection: keep-alive, Upgrade
Sec-Fetch-Dest: empty
Sec-Fetch-Mode: websocket
Sec-Fetch-Site: cross-site
Pragma: no-cache
Cache-Control: no-cache
Upgrad
#ifndef SERVER_H
#define SERVER_H
#define BUFFER_LENGTH 1024
typedef int (*RCALLBACK)(int fd);
// fd and its callbacks, along with buffers to support cbs
struct connection {
int fd;
char rbuffer[BUFFER_LENGTH];
int rlength;
char wbuffer[BUFFER_LENGTH];
int wlength;
RCALLBACK send_callback;
// handle EPOLLIN
// for listen_fd it's used for accepting connection
// for client_fd it's used for receiving data
RCALLBACK recv_callback;
int status; // ws connection state
char *payload; // ws payload
char mask[4];
};
int ws_request(struct connection *);
int ws_response(struct connection *);
#endif
#include <signal.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/epoll.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include "server.h"
// the client will try to create a million conection
// the connection size needs to be bigger than a million
// because we are also using fd as index and new fd doesn't
// start from 0
#define CONNECTION_SIZE 1012000
// for port cycling
#define MAX_PORTS 30
#define TIME_SUB_MS(tv1, tv2) ((tv1.tv_sec - tv2.tv_sec) * 1000 + (tv1.tv_usec - tv2.tv_usec) / 1000)
struct timeval ts;
int listen_fds[MAX_PORTS] = {0};
void handle_signal(int sig) {
int i;
printf("\nserver closing...\n");
for (i = 0; i < MAX_PORTS; i++) {
int fd = listen_fds[i];
if (fd > 0) {
printf("[%d] closing fd %d\n", i, fd);
close(fd);
};
}
printf("bye\n");
exit(0);
}
int init_server(unsigned int port) {
int listen_fd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
if (listen_fd == -1) {
perror("socket");
return -1;
}
// define server address: ip + port
struct sockaddr_in server_addr;
server_addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
server_addr.sin_port = htons(port);
server_addr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY);
// bind and listen for connection
int status = bind(listen_fd, (struct sockaddr *) &server_addr, sizeof(server_addr));
if (status == -1) {
perror("bind socket");
return -1;
}
listen(listen_fd, 10); // allows 10 queued connections
return listen_fd;
}
int epfd;
int accept_cb(int);
int recv_cb(int);
int send_cb(int);
// where we define fd and its callbacks for handling events
// use fd as index
struct connection connection_list[CONNECTION_SIZE] = {0};
// flag determines whether ADD (if non-zero) or MODIFY
int set_event(int fd, int events, int flag) {
int ctl;
if (flag) ctl = EPOLL_CTL_ADD;
else ctl = EPOLL_CTL_MOD;
struct epoll_event ev;
ev.events = events;
ev.data.fd = fd;
return epoll_ctl(epfd, ctl, fd, &ev);
}
int register_event(int fd, int events) {
if (fd < 0) return -1; // otherwise may get "Segmentation fault (core dumped)"
connection_list[fd].fd = fd;
connection_list[fd].recv_callback = recv_cb;
connection_list[fd].send_callback = send_cb;
// reset buffers since fd can be reused
memset(connection_list[fd].rbuffer, 0, BUFFER_LENGTH);
connection_list[fd].rlength = 0;
memset(connection_list[fd].wbuffer, 0, BUFFER_LENGTH);
connection_list[fd].wlength = 0;
// listen for event (readability)
set_event(fd, events, 1);
return 0;
}
int connections = 0;
int accept_cb(int fd) { // listen_fd
struct sockaddr_in client_addr;
socklen_t len = sizeof(client_addr);
int client_fd = accept(fd, (struct sockaddr *)&client_addr, &len);
if (client_fd == -1) {
perror("accept");
return -1;
}
register_event(client_fd, EPOLLIN);
connections++;
// shows the number of connections
// and the time to create them
if (connections % 1000 == 0 || connections > (CONNECTION_SIZE - 1000)) {
struct timeval now;
gettimeofday(&now, NULL);
int ts_elapsed = TIME_SUB_MS(now, ts);
memcpy(&ts, &now, sizeof(struct timeval));
// printf("number of connections: %d, time elapsed: %dms\n", connections, ts_elapsed);
}
return 0; // success
}
int recv_cb(int fd) {
int count = recv(fd, connection_list[fd].rbuffer, BUFFER_LENGTH, 0);
if (count == 0) { // EOF, close connection
// printf("disconnect fd %d\n", fd);
close(fd);
epoll_ctl(epfd, EPOLL_CTL_DEL, fd, NULL);
return 0;
} else if (count < 0) {
printf("client disconnect: %d\n", fd);
close(fd);
epoll_ctl(epfd, EPOLL_CTL_DEL, fd, NULL);
return 0;
}
connection_list[fd].rlength = count;
// echo to wbuffer (response)
// connection_list[fd].wlength = count;
// memcpy(connection_list[fd].wbuffer, connection_list[fd].rbuffer, connection_list[fd].wlength);
ws_request(&connection_list[fd]);
set_event(fd, EPOLLOUT, 0); // modify
// clear the read buffer for the next read otherwise it may contains data from the last ready
memset(connection_list[fd].rbuffer, 0, BUFFER_LENGTH);
return count;
}
int send_cb(int fd) {
int count = 0;
ws_response(&connection_list[fd]);
if (connection_list[fd].wlength > 0) {
count = send(fd, connection_list[fd].wbuffer, connection_list[fd].wlength, 0);
}
set_event(fd, EPOLLIN, 0);
return count;
}
int main() {
signal(SIGPIPE, SIG_IGN); // trap broken pipes
signal(SIGINT, handle_signal); // handle Ctrl+C (SIGINT)
gettimeofday(&ts, NULL);
unsigned short port = 8001;
epfd = epoll_create(1);
int i;
for (i = 0; i < MAX_PORTS; i++) {
int listen_fd = init_server(port + i);
if (listen_fd == -1) return -1;
listen_fds[i] = listen_fd; // register for cleanup
connection_list[listen_fd].fd = listen_fd;
connection_list[listen_fd].recv_callback = accept_cb;
set_event(listen_fd, EPOLLIN, 1);
}
while(1) { // main loop
struct epoll_event events[1024] = {0};
int nready = epoll_wait(epfd, events, 1024, -1);
int i;
for (i = 0; i < nready; i++) {
int fd = events[i].data.fd;
// may handle read and write in the same iteration
if (events[i].events & EPOLLIN) {
connection_list[fd].recv_callback(fd); // either accept or recv depending on lt's listen_fd or client_fd
}
if (events[i].events & EPOLLOUT) {
connection_list[fd].send_callback(fd);
}
}
}
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include <openssl/sha.h>
#include <openssl/pem.h>
#include <openssl/bio.h>
#include <openssl/evp.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "server.h"
#define GUID "258EAFA5-E914-47DA-95CA-C5AB0DC85B11"
#define WEBSOCK_KEY_LENGTH 19
// represents the base ws frame header
struct ophdr {
unsigned char opcode : 4; // opcode field (4 bits)
unsigned char rsv3 : 1; // reserved field 3 (1 bit)
unsigned char rsv2 : 1; // reserved field 2 (1 bit)
unsigned char rsv1 : 1; // reserved field 1 (1 bit)
unsigned char fin : 1; // final frame indicator (1 bit)
unsigned char payload_length : 7; // payload length field (7 bits)
unsigned char mask : 1; // mask bit (1 bit)
} __attribute__ ((packed)); // ensure the compiler doesn't add padding between fields,
// so the struct matches the ws header format exactly
// represents a ws frame with an extended payload length
// of 126 bytes or more
struct websocket_head_126 {
unsigned short payload_length;
char mask_key[4];
unsigned char data[8];
} __attribute__ ((packed));
// represents a ws frame with a payload length
// of 127 bytes or more
struct websocket_head_127 {
unsigned short payload_length;
char mask_key[4];
unsigned char data[8];
} __attribute__ ((packed));
typedef struct ophdr ophdr;
typedef struct websocket_head_126 websocket_head_126;
typedef struct websocket_head_127 websocket_head_127;
int encode_base64(char *in_str, int in_len, char *out_str) {
BIO *b64, *bio;
BUF_MEM *bptr = NULL;
size_t size = 0;
if (in_str == NULL || out_str == NULL) return -1;
b64 = BIO_new(BIO_f_base64());
bio = BIO_new(BIO_s_mem());
bio = BIO_push(b64, bio);
BIO_write(bio, in_str, in_len);
BIO_flush(bio);
BIO_get_mem_ptr(bio, &bptr);
memcpy(out_str, bptr->data, bptr->length);
out_str[bptr->length - 1] = '\0';
size = bptr->length;
BIO_free_all(bio);
return size;
}
int readline(char *buf, int level, char *linebuf) {
int len;
for (len = strlen(buf); level < len; level++) {
if (buf[level] == '\r' && buf[level+1] == '\n')
return level + 2;
else
*(linebuf++) = buf[level];
}
return -1;
}
void unmask(unsigned char *data, int len, char *mask) {
int i;
for (i = 0; i < len; i++) {
*(data+i) ^= *(mask+(i%4));
}
}
unsigned char* decode_packet(unsigned char *stream, char *mask, int length, int *result) {
ophdr *hdr = (ophdr *)stream;
unsigned char *data = stream + sizeof(ophdr);
int size = 0;
int start = 0;
int i = 0;
if ((hdr->mask & 0x7F) == 126) {
websocket_head_126 *hdr126 = (websocket_head_126 *)data;
size = hdr126->payload_length;
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
mask[i] = hdr126->mask_key[i];
}
start = 8;
} else if ((hdr->mask & 0x7F) == 127) {
websocket_head_127 *hdr127 = (websocket_head_127 *)data;
size = hdr127->payload_length;
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
mask[i] = hdr127->mask_key[i];
}
start = 14;
} else {
size = hdr->payload_length;
memcpy(mask, data, 4);
start = 6;
}
*result = size;
unmask(stream+start, size, mask);
return stream + start;
}
int encode_packet(char *buffer, char *mask, char *stream, int length) {
ophdr head = {0};
head.fin = 1;
head.opcode = 1;
int size = 0;
if (length < 126) {
head.payload_length = length;
memcpy(buffer, &head, sizeof(ophdr));
size = 2;
} else if (length < 0xffff) {
websocket_head_126 hdr = {0};
hdr.payload_length = length;
memcpy(hdr.mask_key, mask, 4);
memcpy(buffer, &head, sizeof(ophdr));
memcpy(buffer+sizeof(ophdr), &hdr, sizeof(websocket_head_126));
size = sizeof(websocket_head_126);
} else {
websocket_head_127 hdr = {0};
hdr.payload_length = length;
memcpy(hdr.mask_key, mask, 4);
memcpy(buffer, &head, sizeof(ophdr));
memcpy(buffer+sizeof(ophdr), &hdr, sizeof(websocket_head_127));
size = sizeof(websocket_head_127);
}
memcpy(buffer+2, stream, length);
return length + 2;
}
int hankshake(struct connection *c) {
char linebuf[1024] = {0};
int idx = 0;
char sec_data[128] = {0};
char sec_accept[32] = {0};
do {
memset(linebuf, 0, 1024);
idx = readline(c->rbuffer, idx, linebuf);
if (strstr(linebuf, "Sec-WebSocket-Key")) {
strcat(linebuf, GUID);
SHA1((unsigned char *)linebuf + WEBSOCK_KEY_LENGTH,
strlen(linebuf + WEBSOCK_KEY_LENGTH),
(unsigned char *)sec_data);
encode_base64(sec_data, strlen(sec_data), sec_accept);
memset(c->wbuffer, 0, BUFFER_LENGTH);
c->wlength = sprintf(c->wbuffer,
"HTTP/1.1 101 Switching Protocols\r\n"
"Upgrade: websocket\r\n"
"Connection: Upgrade\r\n"
"Sec-WebSocket-Accept: %s\r\n\r\n",
sec_accept);
printf("ws response : %s\n", c->wbuffer);
break;
}
} while ((c->rbuffer[idx] != '\r' || c->rbuffer[idx+1] != '\n') && (idx != -1));
return 0;
}
int ws_request(struct connection *c) {
printf("received: %s\nstatus: %d\n", c->rbuffer, c->status);
if (c->status == 0) {
hankshake(c);
c->status = 1;
} else if (c->status == 1) {
char mask[4] = {0};
int res = 0;
c->payload = (char *)decode_packet((unsigned char *)c->rbuffer, c->mask, c->rlength, &res);
printf("data : %s, length : %d\n", c->payload, res);
c->wlength = res;
c->status = 2;
}
return 0;
}
int ws_response(struct connection *c) {
if (c->status == 2) {
c->wlength = encode_packet(c->wbuffer, c->mask, c->payload, c->wlength);
c->status = 1;
}
return 0;
}
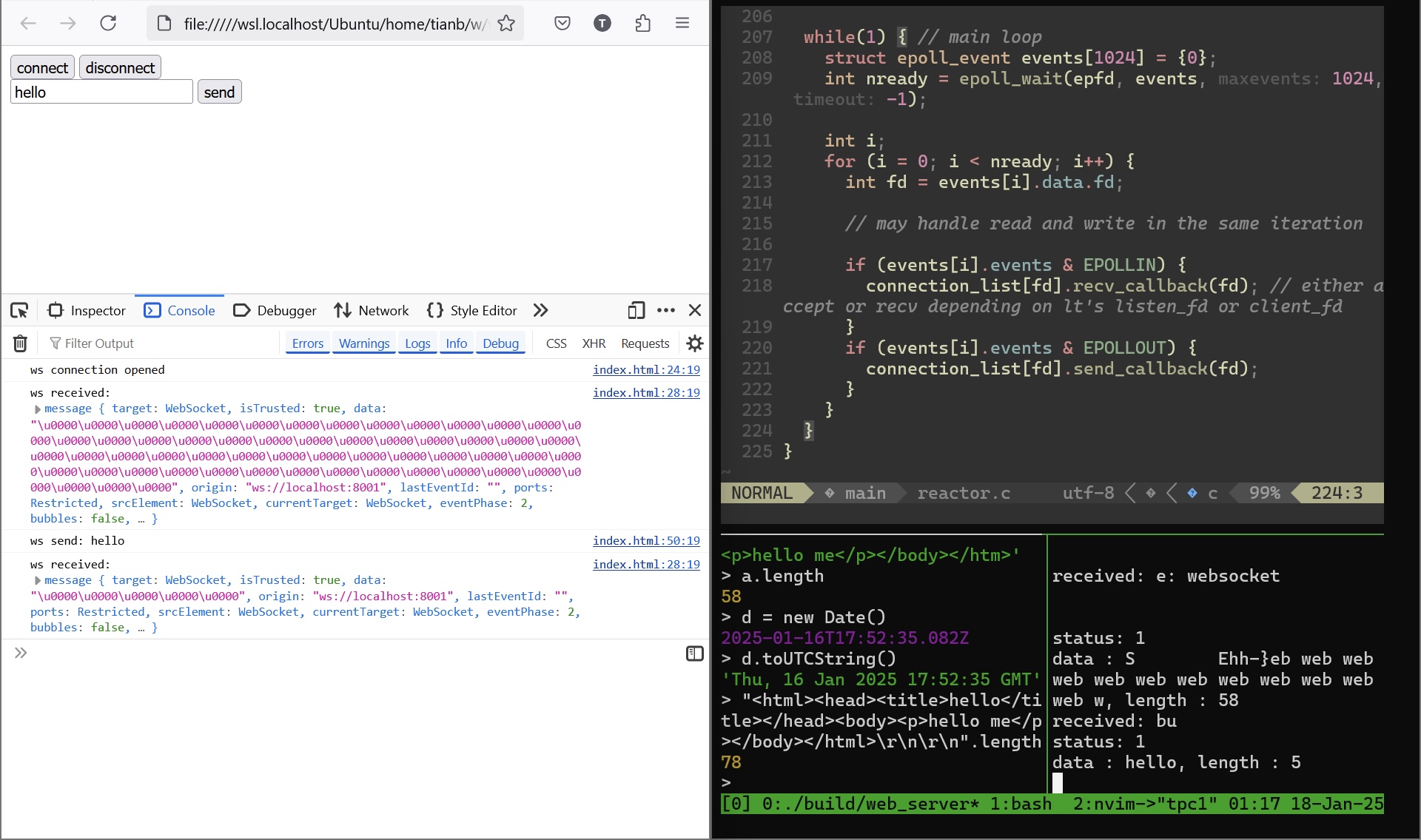
And a minimal WebSocket test client:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title>websocket client</title>
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
</head>
<body>
<div>
<button id="btn-connect">connect</button>
<button id="btn-close">disconnect</button>
</div>
<div>
<input id="ws-msg" type="text" />
<button id="btn-send">send</button>
</div>
<script>
let ws;
function connect() {
if (ws) return;
ws = new WebSocket("ws://localhost:8001");
ws.addEventListener("open", () => {
console.log("ws connection opened");
});
ws.addEventListener("message", (evt) => {
console.log("ws received:", evt);
});
ws.addEventListener("error", (evt) => {
console.error("ws error", evt);
});
ws.addEventListener("close", (evt) => {
console.log("ws connection closed");
});
}
function disconnect() {
if (!ws) return;
ws.close();
ws = undefined;
}
function send() {
const msg = document.getElementById("ws-msg").value;
if (ws && msg && msg.trim()) {
ws.send(msg);
console.log("ws send:", msg);
}
}
document.getElementById("btn-connect").addEventListener("click", connect);
document.getElementById("btn-close").addEventListener("click", disconnect);
document.getElementById("btn-send").addEventListener("click", send);
</script>
</body>
</html>
Although more details could be added, it appears to work at a basic level.